
Negative Sentiment Towards Vaccines Has Increased Since the COVID-19 Pandemic
Environics Analytics’ recently updated VaccinePlus database indicates that a general shift in vaccine sentiment has occurred across the country as result of the COVID-19 pandemic. This may have implications for how the population decides to participate in ongoing and future vaccine programs and how medical professionals, vaccine manufacturers and government agencies manage expectations around vaccines in the future.
The results show that today, 82% of Canadian’s feel positively about receiving future vaccines in general, while 18% feel the opposite. This is a growth of 4% in negative sentiment since the pandemic began. Different groups of people and different parts of the country had varying responses to the ongoing developments during the pandemic. And while some were adversely affected from a health perspective, others were impacted financially or socially as well.
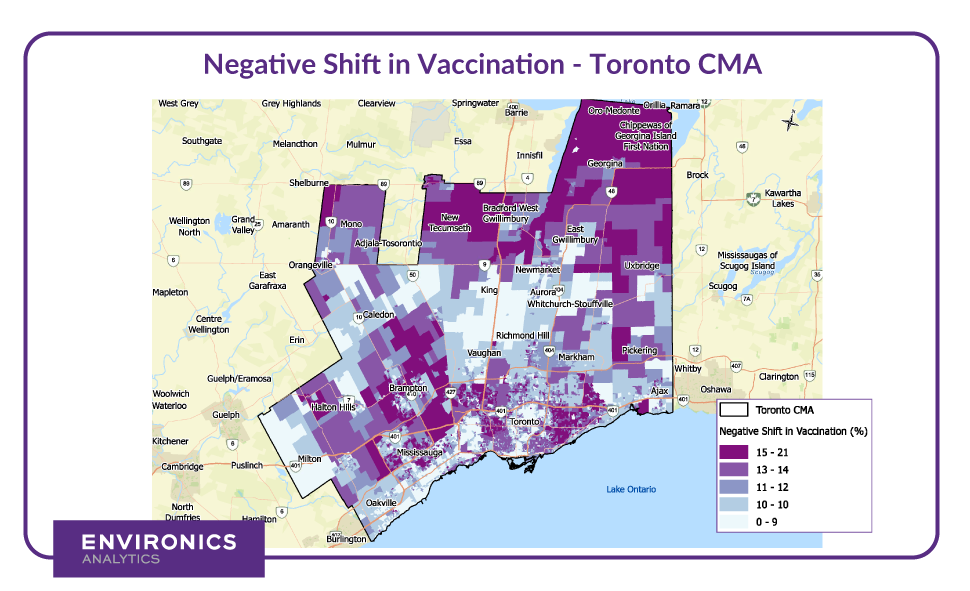
Using PRIZM® lifestyle segmentation, connected with demographic and psychographic data, we can dig deeper and profile the groups that have changed their sentiment towards vaccines and identify the key indicators for negative sentiment. Furthermore, we can identify if there are specific areas of the country that have experienced this change in sentiment more than others and understand how to potentially help change their minds or communicate more effectively in the future.

Key social values among those with increased negative vaccine sentiment
EA's SocialValues database helps users understand the mindset of their customers and determine the best message to engage them. Some mindsets based on vaccine sentiment can include:
- Technological Anxiety
- Low confidence in large businesses
- Rejection of Authority
- Religiosity
- Poor Effort Towards Health
- Alternative views towards mainstream healthcare
Small-town sensibility
A group of those experiencing one of the highest levels of negative shift in openness to receiving future vaccinations are older families living in rural communities in the Prairies, Atlantic provinces and territories.
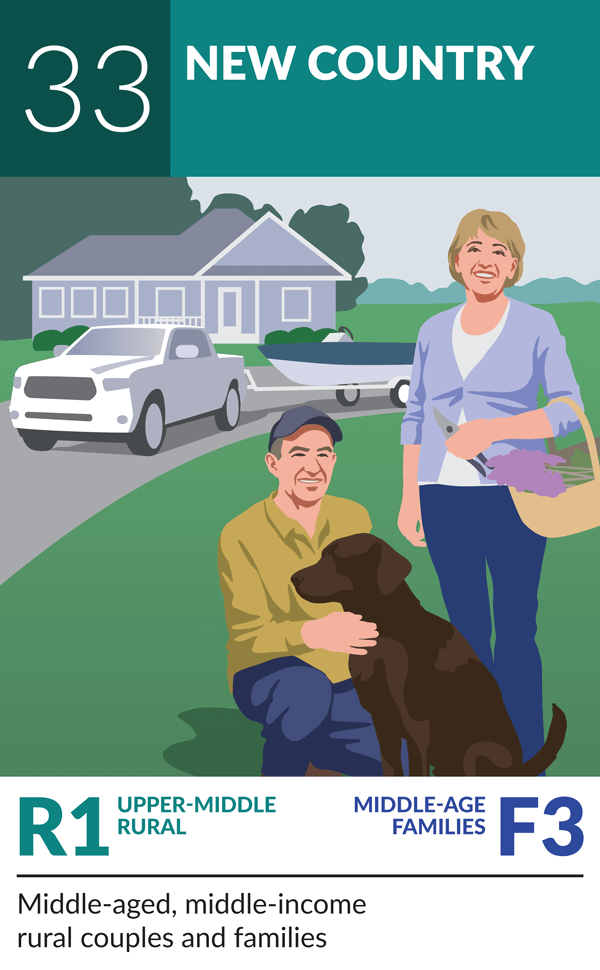



They are likely to be high school educated, some of whom have attended community college or trades programs. If not retired, then they are likely to work blue-collar jobs or service jobs earning household incomes slightly below the Canadian average allowing them to be comfortable financially but not in a place to whether income loss or additional expenses without stress. They prefer to have simple lives so tend to shy away from large technological advancements and have strong religious beliefs. When it comes to their health, although most have access to a regular healthcare provider, they don’t prioritize an overly healthy way of life. Data also shows a significant drop in those having received the flu shot this year when compared to last year.
Based on these traits, it is likely that new vaccine technology and confusing communications may have been some reasons for this group becoming more hesitant towards receiving future recommended vaccines. They work in careers that were impacted heavily during lock downs, causing financial stress on top of the health risks that may have also contributed to the negativity.
City state of mind
Another group that developed negative sentiments towards vaccination since the pandemic is a distinct set of younger singles and couples living in urban centres and are found across the country with the exception of Quebec.
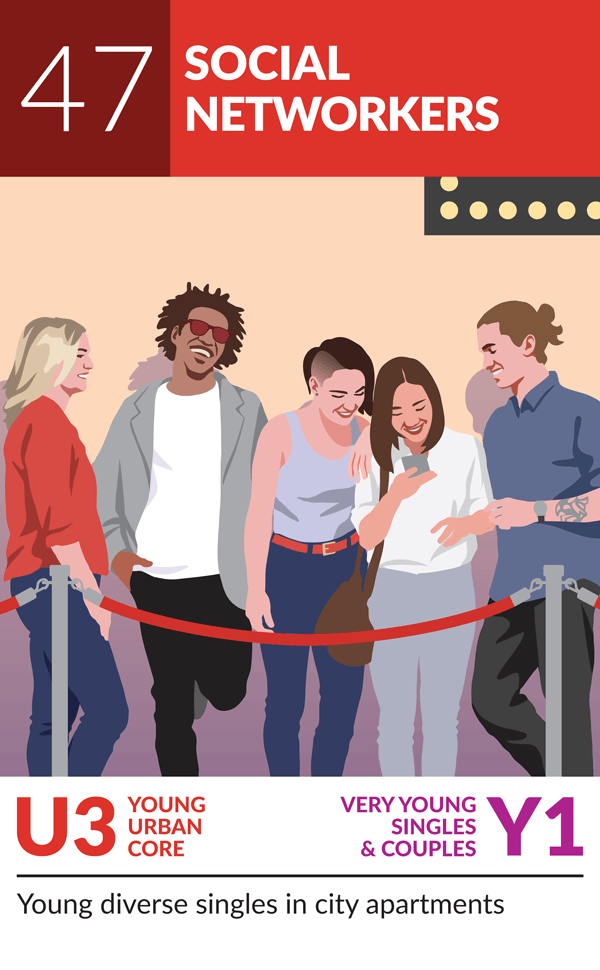

Many in this group work service jobs and may struggle day-to-day with the rising costs to live in the cities they call home. During the pandemic, it is likely that they were either working the front lines or laid off temporarily, adding more stress to the situation by creating financial strain.
While this group tends to hold contemporary, liberal values, they possess a strong urge to reject authority and also tend to be quite cynical, particularly towards big businesses like large pharmaceutical companies, the government and healthcare providers. These are young, social individuals and the lockdowns likely didn’t help their attitudes, leaving them feeling isolated, often in smaller apartment style dwellings.
When it comes to their health, this group is more likely to not have access to a regular healthcare provider and tends to prefer using natural remedies when possible as they fear contents of non-natural remedies and prefer alternative approaches to healthcare. Additionally, new developments in vaccine technology and unclear government ordinances are all likely contributors to their newfound hesitancy towards future vaccine recommendations, but negative feelings on how the pandemic was handled may also be a driver of this change.
While there has been a shift in negative sentiment towards future general vaccination with distinct groups of Canadians since the pandemic began, it is clear from the analysis above that different groups adopted this stance for different reasons. Leveraging data from Environics Analytics, health and pharma organizations can better understand and reach these groups with relevant communications to suit their needs and to help change their minds.
These data also show that certain groups in the country who were previously more hesitant in general towards vaccines had the complete opposite occur since the pandemic are now more open that ever to future vaccine recommendations. Learn who these groups are and how to connect with them as well as which groups have remained open to vaccines and would align best with your brand.
Get in touch to learn how you can leverage data, analytics and insights to uncover a multitude of answers to your business questions, make informed decision-making and achieve your goals and objectives.
Related Content
Learn more about data analytics for pharma and healthcare
Learn more about PRIZM® segmentation
* PRIZM® is a registered trademark of Claritas, LLC.


